
Open RAN Series: Open RAN Intelligence (Part 3 of 3)
May 6, 2021
In Parts 1 & 2 of our series we looked at “What is Open RAN?” and how “Open RAN is sowing the seeds of innovation” as the momentum grows globally for Open RAN technology. In this third and final part of our series, we look at the critical role built-in intelligence will play to ensure the optimal performance of Open RAN.
The advantages of disaggregation of the RAN for MNOs, such an increased and diverse vendor eco-system and the expected CAPEX/OPEX savings for example, need to be balanced against the added complexity of managing a RAN which most likely will now be a system composed of Network Elements (NE) and Network Functions (NF) from many different vendors. However, the MNOs should be shielded from such complexity and key to this is embedding intelligence within the NEs such that the Open RAN will be Zero Touch/Self- Healing.
As can be seen in figure 1, the O-RAN logical architecture introduces the RAN Intelligent Controller, which consists of a Non-Real-time Controller (supporting tasks that require >= 1s latency) and a Near-Real Time controller (latency of >= 10ms < 1s).
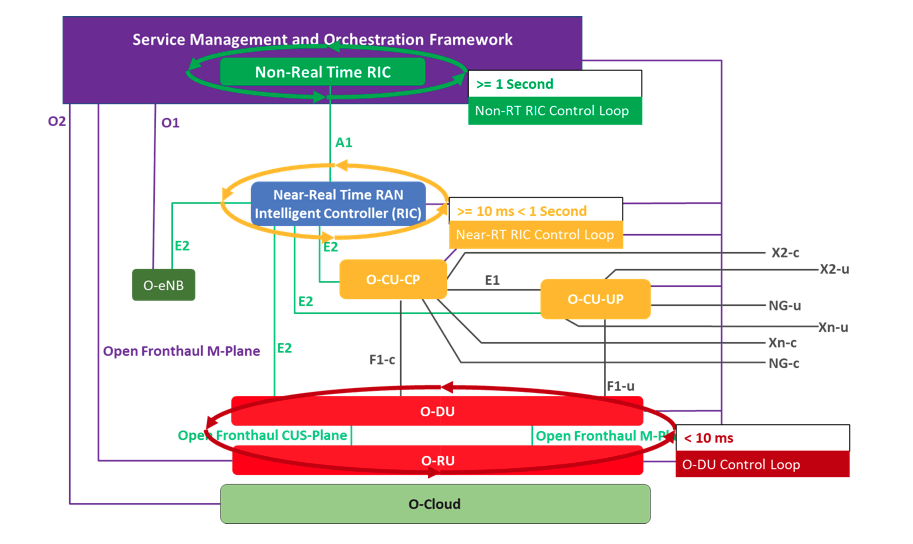
Figure 1: O-RAN logical architecture
The Near Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Near-RT RIC) is a software platform which hosts micro-service-based applications called xApps. The Near-RT RIC leverages a Radio-Network Information Base (R-NIB) database which captures the near real-time state of the underlying network to provide typical Radio Resource Management (RRM) for the distributed RAN infrastructure CU and DU NE/NF via the southbound E2 protocol. This means that the RRM which drives the system, and which has typically been embedded within the Base Band, can now be disaggregated from the CU vendor software, with MNOs having the possibility to deploy own in-house or best of breed 3rd party xApps.
The Near-RT RIC can be deployed in a centralized or distributed model, depending on network topology. Given those 5G use cases which require ultra-low latency, such as autonomous vehicles, the Near-RT RIC can be deployed at the ‘edge’, and indeed the Radio Network Information Service of the Multi-Access Edge Compute (MEC) described by ETSI has a lot of synergy with the Near-RT RIC.
The Near-RT RIC also provides the “northbound” A1 and O1 interfaces towards the Non Real-Time RAN Intelligent Controller (Non-RT RIC) for the management and self-optimization/healing of the E2 nodes within the RAN. The Non-RT RIC comprises a platform plus a set of (micro)services named rAPPs by O-RAN Alliance that represent the intelligence needed to support intelligent RAN optimization by providing policy-based guidance, model management and enrichment information to the Near-RT RIC function so that the RAN can be optimized.
The design of the system is based on:
- Enrichment information with potential to improve the RRM and RAN performance in general. This includes application-level information, cross-domain information, UE positions and mobility trajectories as well as external information.
- Use of AI/ML from day 1 for optimised control of RAN.
- Dynamic optimization of the RAN on a timescale down to seconds.
- An open eco-system of intelligent controller software where 3rd Party rAPPs feed each other with data and insights
All the data (both RAN and external) available to the Non-RT RIC is used to train the AI/ML models, which are then fed to the Near-RT RIC via A1 interface to facilitate more optimised radio resource management for the RAN performance.
While it is the O-RAN Alliance which is defining/standardising the Non and Near Real Time RIC, there are development communities who are working on realisation of the respective platforms. The O-RAN Software Community is partnering with the O-RAN Alliance and Linux Foundation to support the development for open RAN near-RT/non-RT RIC solutions, and is working on delivering sample xApps (mobility, QoS management, traffic steering and KPI monitoring) and rApps (Traffic steering, QoE, QoS based resource optimisation and Context-based dynamic handover management for V2X) addressing Use Cases. Also, the SD-RAN project in Open Network Foundation (ONF) first release of the SD-RAN project from January 2021 implements a near-RT RIC called µONOS.
What is clear is that Intelligence will at the core of successful Open RAN commercial deployments, and given our heritage in development of 3G/4G/5G RRM and AI/ML solutions within Aspire Technology, we look forward to working with the O-RAN Alliance and our fellow members to bring this to fruition.






